Les opérateurs simples |
|
Les opérateurs de base
Propriétés
Les opérateurs "intermédiaires"
Table des matières
Index
- Porte ET (AND)
-
- Schéma :
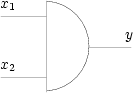
- Table de vérité :
x2\x1 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 - Notation : y=x1.x2
- Schéma :
- Porte OU (OR)
-
- Schéma :
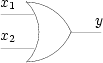
- Table de vérité :
x2\x1 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 -
Notation : y=x1
 x2 ou y=x1+x2. Attention, cette dernière notation n'a rien à voir avec une addition ; par exemple, dans ces conditions, 1+1=1.
x2 ou y=x1+x2. Attention, cette dernière notation n'a rien à voir avec une addition ; par exemple, dans ces conditions, 1+1=1.
- Schéma :
- Porte NON (NOT(1))
-
- Schéma :
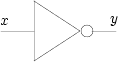
- Table de vérité :
x 0 1 y 1 0 - Notation : y=x
- Schéma :
- Cette opération est aussi appelée complémentation.
Retour au texte
|
Copyright 2000-2010 G. Chagnon Copyright (c) 2001-2010 Gilles Chagnon. Ce document est publié selon les termes de la GNU Free Documentation License (version française). |
|
http://www.gchagnon.fr/cours/courlong/5_2_1_1.html